Understanding and Maintaining Private Wells
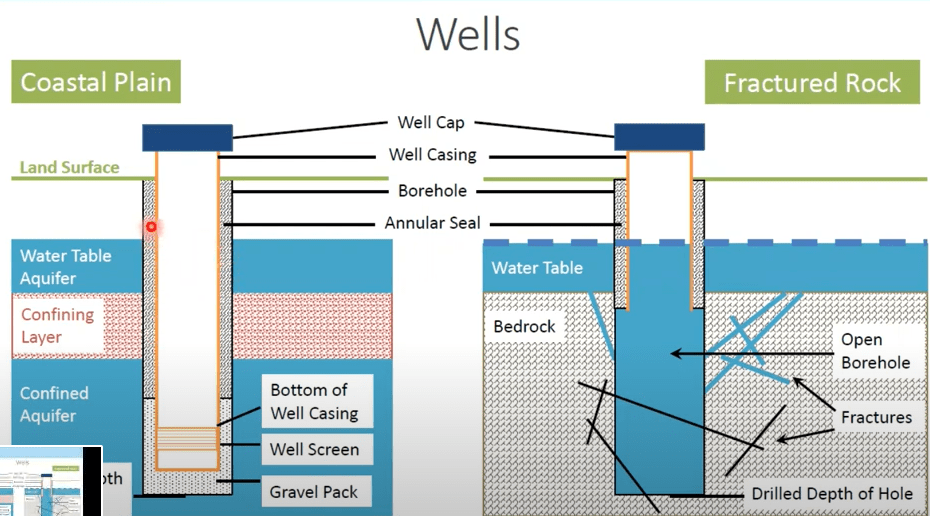
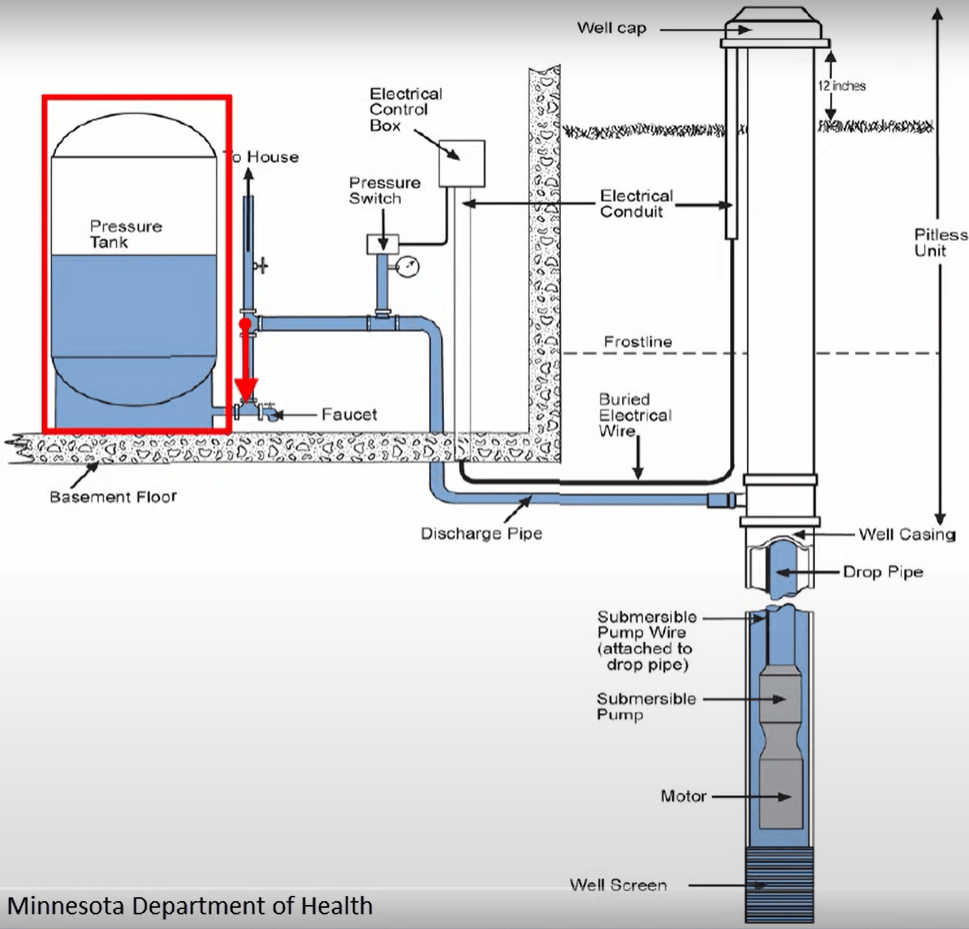
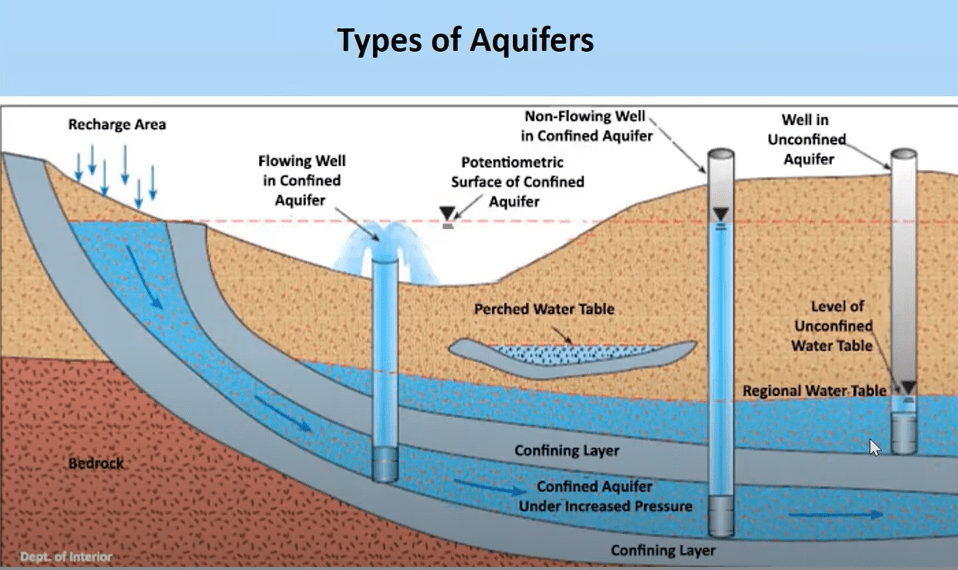
Schematic of a Well
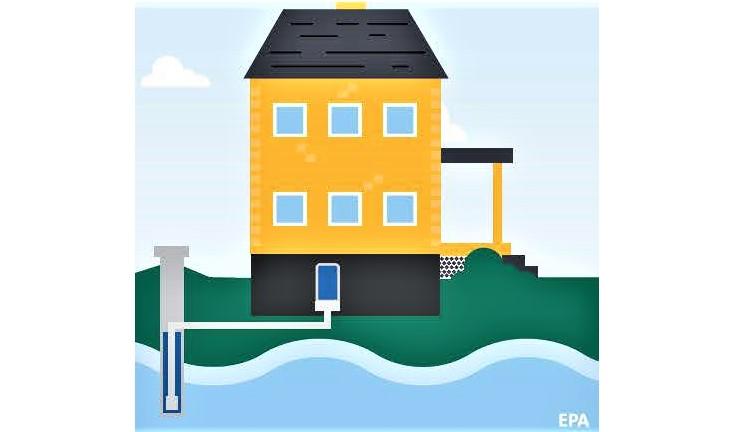
One of the easiest ways to prevent your drinking water from getting contaminated is to familiarize yourself with your well and routinely inspect the visible components of the well. The first step is to check your well log, the report submitted to your county officials after the well has been constructed and inspected. If you do not have your well log, also known as the well completion report, you can contact your county office to request a copy.
Your well log will include information on all of the components of the well. You can refer to our glossary to familiarize yourself with the main components of the well. The only components that will be visible to you are the ones at the wellhead, which include the casing and well cover. When inspecting your wellhead, you want to make sure that the ground slopes away from the wellhead. Read further for more inspection tips.
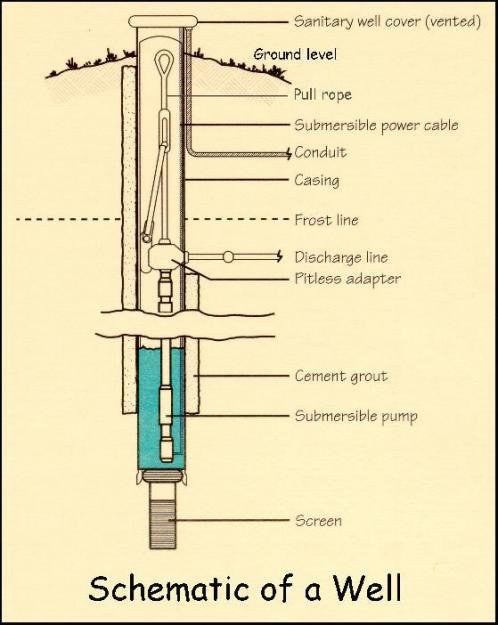
Anatomy of a Well
| PART | LOCATION | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|
| CASING | Metal or plastic pipe that line a portion of the bore hole. | Depending on the surrounding area, state regulations determine the depth for the casing. In general, it must extend a minimum of 8 inches above the ground, or 24 inches in flood zones, to keep storm water runoff out of the well. You should also check to make sure that the casing is in good condition (no cracks, dents, etc.). |
| GROUT | Material that seals the bore hole and the casing. | An airtight seal prevents surface water and contaminants from running down the side of the well. Depending on state regulations, a professional may apply grout made from portland, quick-setting cement or bentonite clay. |
| WELL COVER | A cap on top of the well casing. | The cover, which either clamps or screws onto the well casing, prevents contaminants from entering the well. When inspecting your wellhead, make sure that the well cap is in good condition and tightly secured. We recommend using a sanitary well cap, which includes a rubber gasket and vented screen to prevent contamination and used nuts and bolts for security. |
| SCREEN | A filter at bottom of a drilled well. | A well screen is a filtering device located at the bottom of the well casing. They allow water to move through the well, while keeping out most gravel and sand. |
| PUMP | Motor system that moves water into the distribution system from the bottom of the well. | If the well is close to loose sand or fragmented rock, the screen allows water in but keeps sand and sediment out, through openings along the bottom. If the well is drilled in bedrock, a screen is not usually required but may be necessary. |
| PITLESS ADAPTER | Adapter located below the frost line. | Provides a frostproof and sanitary hookup between the well and the household water distribution system. |
Helpful Resources